Domestic Violence in India: Legal Rights & Protection Guide 2025
Domestic violence is not just a personal problem. It is a serious legal and social issue affecting countless individuals across India. It goes beyond physical abuse, including emotional trauma, financial control, and psychological intimidation. If you or someone you know is in this situation, take action immediately. Learn about your rights and the legal protections under the Domestic Violence Act, 2005.
Seeking Immediate Legal Help?
Contact Aditya & Co. Advocates – Your Constant Legal Guardian. Call +91 8105812404 for a free consultation.
What is Domestic Violence?

Domestic violence refers to any form of abuse or harmful behavior within a household. It typically happens between spouses or family members. It includes:
- Physical Abuse: Hitting, slapping, pushing, or causing physical harm.
- Emotional Abuse: Insults, threats, humiliation, and mental harassment.
- Sexual Abuse: Unwanted sexual contact or coercion.
- Economic Abuse: Restricting access to finances or resources to control the victim.
In India, the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005, provides critical legal support. It helps victims of abuse seek immediate protection and justice.
Common Misconceptions About Domestic Violence Laws
Despite strong legal provisions, several myths around domestic violence still exist. Understanding these misconceptions is crucial for victims to take informed legal action and for society to support them effectively.
|
Myth |
Fact |
|---|---|
|
Only married women can file domestic violence cases. |
Any woman in a domestic relationship can seek protection under the Domestic Violence Act, 2005. This includes women in live-in relationships. |
|
Domestic violence only includes physical abuse. |
Emotional, economic, and sexual abuse also qualify as domestic violence. |
|
Filing a domestic violence complaint will immediately lead to an arrest. |
The Act primarily focuses on protection and rehabilitation, not just criminal punishment. |
What Does the Domestic Violence Act 2005 Say?
The Domestic Violence Act, 2005, is a powerful legal tool designed to protect victims, especially women. Key provisions include:
- Right to Residence: A woman cannot be forced out of her marital home, even if she doesn’t legally own it.
- Protection Orders: Courts can restrict the abuser from contacting or approaching the victim.
- Monetary Relief: Compensation for financial losses due to abuse.
- Child Custody Orders: Courts prioritize the safety and well-being of children involved.
This Act focuses on providing immediate relief and safety rather than just criminal prosecution.
Types of Domestic Violence You Should Know
Recognizing the different forms of abuse is the first step to taking action:
- Physical Violence: Assault, beatings, or causing bodily harm.
- Emotional and Psychological Abuse: Constant criticism, threats, or isolation.
- Sexual Abuse: Forced sexual activities or marital rape (partially criminalized in India).
- Economic Abuse: Denying financial independence or controlling resources.
If you’re experiencing any of these, know that the law is on your side.
Causes of Domestic Violence

Understanding the causes of domestic violence can help identify early warning signs and prevent escalation. Common causes include:
- Cultural and societal acceptance of male dominance.
- Economic stress and unemployment.
- Addiction issues like alcohol or drug abuse.
- Psychological disorders or past trauma.
- Lack of legal awareness and social support.
Addressing these underlying issues is critical in breaking the cycle of abuse.
Effects of Domestic Violence on Mental Health
Domestic violence has a profound impact on mental health, leading to:
- Anxiety and depression.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Low self-esteem and self-worth.
- Social isolation and trust issues.
Counseling and therapy are essential for emotional recovery and long-term healing.
How Domestic Violence Affects Children
Children who witness or experience domestic violence often suffer long-term psychological and emotional effects. These can include:
- Behavioral problems and aggression.
- Poor academic performance.
- Fear and insecurity in relationships.
- Anxiety and depression.
Protecting children from abusive environments is crucial for their healthy development.
Legal Steps to Take if You Face Domestic Violence

If you’re in immediate danger, your safety should be the top priority.
- Call for Help:
- Women’s Helpline: 1091
- National Domestic Violence Helpline: 181
- Police Emergency: 100 or 112
- Women’s Helpline: 1091
- File an FIR at the Nearest Police Station:
- Under Section 498A IPC (Cruelty by husband or in-laws).
- Other applicable sections: Section 323 IPC (Causing Hurt), Section 506 IPC (Criminal Intimidation).
- Under Section 498A IPC (Cruelty by husband or in-laws).
- Seek a Protection Order:
- Approach the Magistrate through a Protection Officer or with the help of a lawyer.
- Approach the Magistrate through a Protection Officer or with the help of a lawyer.
- Collect Evidence:
- Maintain a diary of abuse incidents.
- Save threatening messages, emails, and social media posts.
- Obtain medical reports if injured.
- Maintain a diary of abuse incidents.
How to Get Interim Maintenance During Domestic Violence Cases
Victims of domestic violence can seek financial support through interim maintenance while legal proceedings are ongoing. Under Section 24 of the Hindu Marriage Act, courts can grant maintenance to cover living expenses and legal fees. Victims can also seek compensation under Section 125 CrPC and the Domestic Violence Act, 2005.
Impact of Domestic Violence in Divorce Cases
Domestic violence plays a significant role in divorce proceedings, affecting:
- Grounds for Divorce: Under Section 13(1)(ia) of the Hindu Marriage Act, cruelty is a valid ground for divorce.
- Alimony & Maintenance: Victims may receive higher financial compensation for the trauma endured.
- Child Custody: Courts prioritize the child’s safety and may deny custody or restrict visitation rights to abusive parents.
Financial Rights of Domestic Violence Victims
Victims have the right to claim financial relief under:
- Section 20 of the Domestic Violence Act, 2005 for monetary compensation.
- Section 125 CrPC for maintenance.
- Section 24 of the Hindu Marriage Act provides for interim maintenance.
Financial independence is key to breaking free from abusive situations.
How to Collect Strong Evidence for a Domestic Violence Case
- Keep detailed records of each incident – dates, times, and nature of abuse.
- Preserve digital evidence like WhatsApp chats, call recordings, and emails.
- Take photographs of physical injuries and keep medical reports.
Proper documentation strengthens your case and helps courts issue immediate protective orders.
Where to Get Immediate Help?
- Women’s Helpline (1091): For police support in emergencies.
- National Helpline (181): 24/7 support for victims of domestic violence.
- Legal Aid: Contact NALSA or state legal services for free legal help.
Women’s Shelters: Organizations like Sakhi One-Stop Centers offer shelter, counseling, and rehabilitation.
FAQs About Domestic Violence in India
Can I file for divorce solely based on domestic violence?
Yes, you can. Under Section 13(1)(ia) of the Hindu Marriage Act, cruelty due to domestic violence is a valid ground for divorce.
What legal protections are available under the Domestic Violence Act, 2005?
You can seek protection orders, residence rights, monetary relief, and custody orders under the Act.
How does domestic violence affect child custody?
Courts prioritize the child’s safety and well-being. The abusive parent may be denied custody or allowed only supervised visitation.
Can I receive financial assistance if I’m a victim of domestic violence?
Yes, you can receive financial assistance through maintenance under Section 125 CrPC. You can also request interim maintenance under Section 24 of the Hindu Marriage Act. Additionally, you may seek monetary relief under Section 20 of the Domestic Violence Act, 2005.
How can I protect my children from an abusive spouse?
Seek immediate custody orders from the court and request supervised or denied visitation for the abusive parent.
Can a working woman claim maintenance under the Domestic Violence Act?
Yes, even if employed, a woman can claim maintenance. This applies if her earnings are not enough to maintain the lifestyle she enjoyed during marriage.
Can I withdraw a domestic violence case after filing it?
Yes, civil proceedings can be withdrawn. However, criminal charges under Section 498A IPC may require High Court intervention for quashing.
How long does it take to get a protection order?
Courts may issue interim protection orders within a week based on urgency and available evidence.
Is mediation allowed in domestic violence cases?
Yes, but only if the victim agrees. Courts often suggest mediation to reach amicable settlements.
Are there specific shelters or homes for victims?
Yes, Sakhi One-Stop Centres and other government-funded shelters provide safe accommodation and legal assistance.
Landmark Supreme Court Judgments on Domestic Violence
- V.D. Bhanot v. Savita Bhanot (2012):
Held that even women separated from their husbands can seek relief under the Domestic Violence Act. - Shobha Rani v. Madhukar Reddy (1988):
Recognized emotional and mental cruelty as valid grounds for divorce. - Narendra v. K. Meena (2016):
Established that prolonged mental cruelty can be grounds for granting a divorce.
These cases reinforce that the judiciary takes domestic violence seriously and offers strong legal remedies.
How to File an Online Domestic Violence Complaint in India
This guide helps victims of domestic violence in India file online complaints easily. It also explains how to use official government portals for legal protection.
Visit the National Women’s Commission Portal

Go to the official National Commission for Women portal at https://www.ncw.gov.in/. This is the starting point to register your domestic violence complaint online.
Select ‘Register Complaint’ and Fill Details

Choose the ‘Register Complaint’ option and carefully provide your personal information along with accurate details about the incident.
Upload Supporting Documents
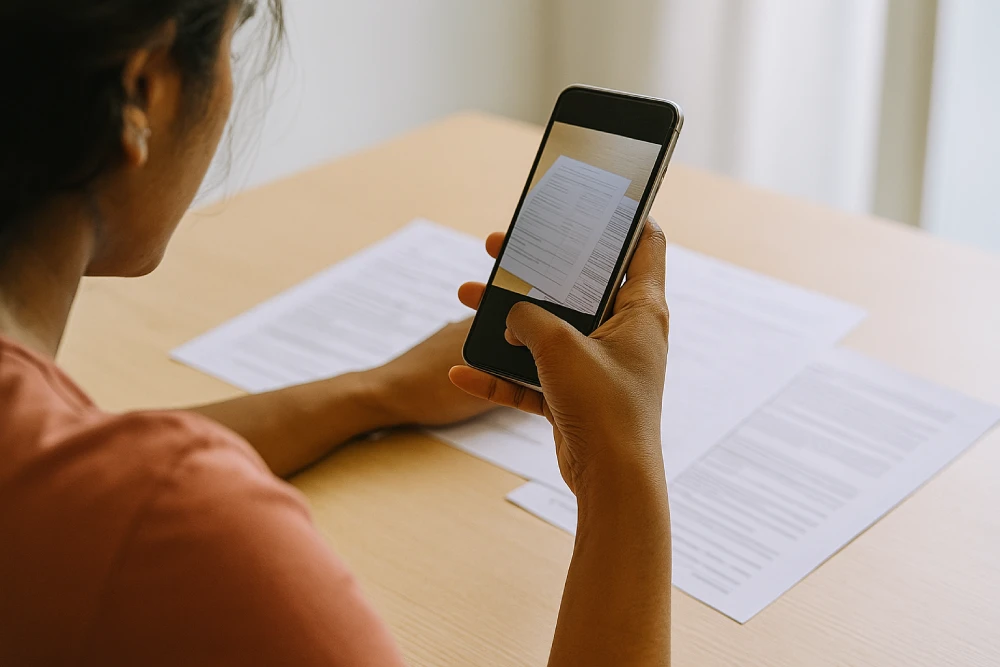

Attach relevant evidence such as medical reports, threatening messages, and photographs of injuries. You can also include any other documents that support your case.
Submit and Note the Complaint Reference Number.
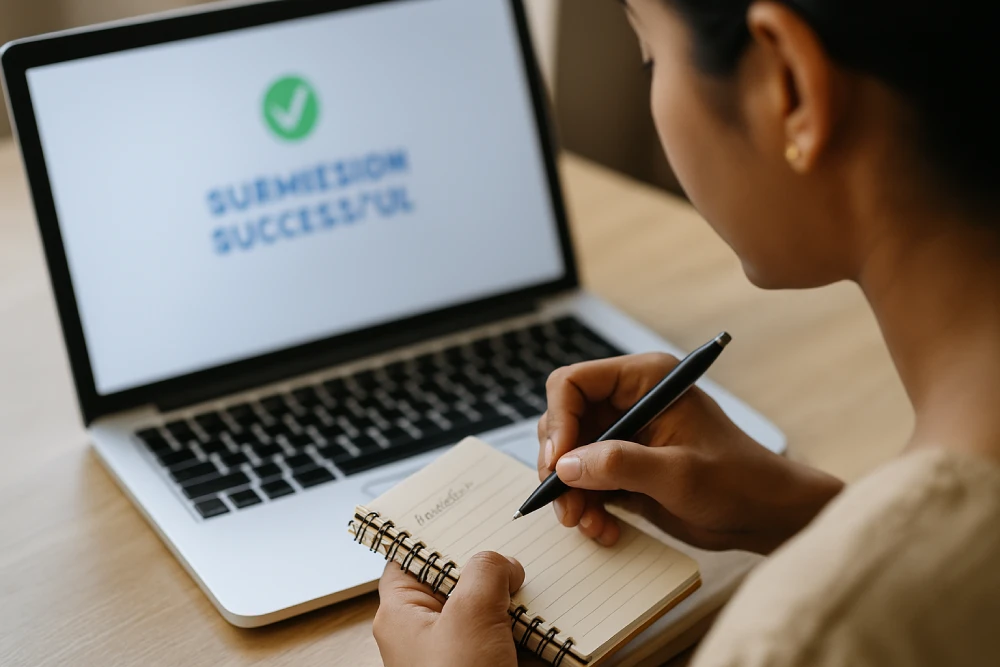

After submitting the complaint, make sure to save or write down the reference number. This will help you track your complaint status later.
Follow Up on Your Complaint
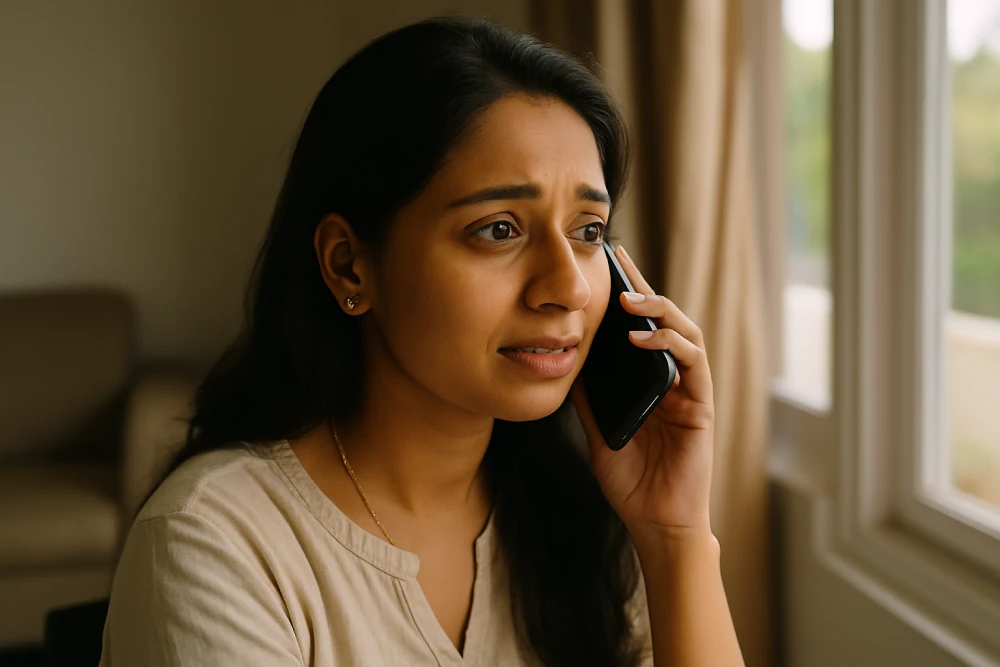

Use the reference number to track your complaint online. You can also call the national helpline at 181 for immediate assistance and updates.
Alternatively, you can directly approach Protection Officers appointed under the Act through District Legal Service Authorities.
Conclusion: You Are Not Alone. Help is Available
If you are trapped in an abusive situation, remember that help is just a call away. Indian law offers powerful protections to help you break free from abuse. It also helps you rebuild your life with dignity and safety.
Need legal guidance? Our experts at Aditya & Co. Advocates are available 24/7. Call us at +91 8105812404







